Headquarters of Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park Management Board
– Address: Phong Nha Town – Bo Trach District – Quang Binh Province
– Phone/Fax: (0232) 3677021
– Email: pnkb@quangbinh.gov.vn
Location: PNKB National Park is located in Quang Binh province, Central region of Vietnam. Geographic coordinates: 17021’12” to 7044’51” North latitude; 105046’33” to 106023’33” East longitude.
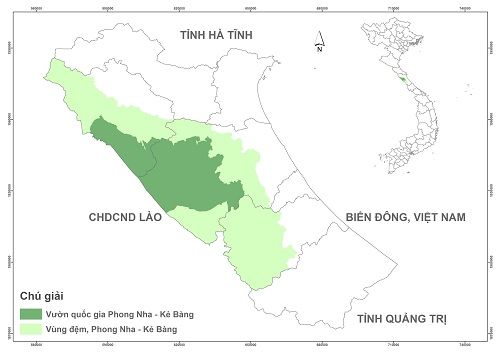
Total area: 123.326 ha. The Park was zoned into three administrative areas: A Strict protection area (100.296 ha), a Forest rehabilitation area (19.619 ha) and a Administration and Services area (3.411 ha).
The buffer zone has an area of 220.055 ha in 13 communes (including Dan Hoa, Hoa Son, Trung Hoa, Thuong Hoa, Trong Hoa communes of Minh Hoa district; Tan Trach, Thuong Trach, Xuan Trach, Phuc Trach, Son Trach, Phu Dinh, Hung Trach communes in Bo Trach district and Truong Son commune in Quang Ninh district
Overview Map of Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park
Establishment: In 2001, Formerly known as Phong Nha Nature Reserve
Recognized by UNESCO: World Natural Heritage; on the criteria: Criterion (viii) on geology and geomorphology (in 2003); Criterion (ix) on ecosystem and (x) on biodiversity (in 2015); In 2025: Inscribed by UNESCO as a Transboundary World Heritage Site “Phong Nha–Ke Bang National Park and Hin Nam No National Park”.
Ranked as a special National Monument (in 2009).
Geology and geomorphology
Phong Nha – Ke Bang is likened to a huge geological museum of universal value and significance. Most of the area is limestone and connects the Hin Namno National Park of Laos to form a large Karst massif in Southeast Asia.
Phong Nha – Ke Bang is the result of the development of 5 geological tectonic periods, from the Ordovician period (464 million years) to the Quaternary. This is demonstrated through complexes of rich and diverse paleontological fossils represent different stratigraphic ages.
Tower of Paleokarst in Phong Nha – Ke Bang
Cave: 447 caves have been surveyed and measured with a total length of 246km. Caves in PNKB are divided into three main systems: Phong Nha system, Vom system and Chay system. Phong Nha cave system is rated as the world’s leading value because it retains the integrity of the values of geology – geomorphology, which was formed from the long-term process of tectonic crust of the Earth. The highlights are Son Doong cave, Phong Nha cave, Tien Son cave, Thien Duong and Hoa Huong cave, etc.
Stalagmite in Va cave
Hydrology: There are three main river, including the Chay, Son and Trooc rivers. All of which are fed by underground streams, which emerge from the En, Vom, Toi and Phong Nha cave systems.
Confluence of Son River
Vegetation: There are 15 large habitat types with 21 important vegetation types. Evergreen forests cover 93.5% of the area, of which over 90% is the largest tropical forest ecosystem on limestone mountains in Southeast Asia and most of it has not been affected.
Primitive forest on limestone mountains
Flora: 2,954 plant species belonging to 1.007 genera, 198 families, 62 orders, 11 classes, 6 phylums have been founded. 112 species listed in the Vietnam Red Book, 121 species listed in IUCN Red Book, 01 species listed in CITES Appendices and 03 species listed in Decree 64/2019/NĐ-CP.
Vietnam incense-cedar area on rocky mountains in Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park
Fauna: 1,399 animal species of 835 genera, 289 families, 66 orders, 12 classes and 4 phyla have been recorded. Of which, there are 84 species are listed in Vietnam Red Book, 110 species are listed in World Red Book (IUCN), 55 species are listed in CITES Appendices and 35 species are listed in Decree 64/2019/ND-CP. Among them, there are a number of rare species such as Ha Tinh langur, brown-shanked douc, white-cheeked Den gibbon, Saola Pseudoryx nghetinhhensis and Large-antlered muntjac.
Red-shanked douc
New species: Phong Nha – Ke Bang is the place where many new species are recorded for science in the early 21st century. 48 new species are discovered for publication worldwide, in which are 43 animal species and 05 plant species.
Khorata protumida – New species of spider was discovered in Bay Tang Cave, Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park
Regarding ethnic groups: Not only Kinh people but also many other ethnic groups living in the area, including 2 main ethnic groups: Chut ethnic group (Sach, May, Ruc, A Rem) and Van Kieu ethnic group (Van Kieu, Khua, Ma Coong, Tri).
Village of Arem people living in Phong Nha – Ke Bang National Park
Historical and cultural relics: Xuan Son ferry, Ho Chi Minh trail, route 20 Quyet Thang, Mu Gia pass, A.T.P key, Tra Ang bridge, Ca Tang, corner of chu A, Ve stream, Cave of Eight Ladies, 9-storey cave, Nguyen Van Troi ferry, Tien su Tu coc Temple
Memorial Temple for Heroes and Martyrs of route 20 Quyet Thang
Festivals and Traditional Culture: Drum festival of Macoong people of Thuong Trach commune on February 16th (According to the Lunar Year); Nghe Temple Festival, Khuong Ha Tuong Boi, New Rice Festival, Asking for the Fairy Water Ceremony and the Full Moon Festival in Minh Hoa district (in March), Forest Opening Ceremony…
Drum festival of Macoong people
Archaeological relics: 33 archaeological sites dating from 3,000 – 12,000 years ago were found in Phong Nha. Some typical relics in Phong Nha – Ke Bang include: Bi Ky cave (belonging to Phong Nha cave) including a Cham altar, 97 ancient characters carved on cliffs, stone statues, ceramic fragments and many tablets containing sacred relics. Champa cultural information. Relics in Hung Trach commune, Son Trach include tombs made of ceramic jars, earrings, and bronze ax blades containing cultural information from Dong Son and Sa Huynh.
Remnants of Cham characters in Phong Nha cave